Unlocking the Canine Code: A Journey Through Dog Training Methods
In a world where dogs are not just pets but cherished members of the family, the art of training these loyal companions has become an essential pursuit for pet owners. Whether you’re welcoming a lively puppy into your home or seeking to refine the behavior of an older canine companion, understanding the diverse landscape of dog training methods is crucial. From time-honored techniques passed down through generations to innovative approaches grounded in behavioral science, the options available can be as varied as the breeds themselves. This article delves into the fascinating array of dog training methods, exploring their principles, practices, and the unique benefits they offer for both dogs and their humans alike. Join us as we embark on this journey to decode the language of our four-legged friends and foster deeper connections through effective training.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Science Behind Positive Reinforcement
- Exploring the Role of Consistency in Effective Dog Training
- Tailoring Training Techniques for Different Breeds and Temperaments
- Navigating Common Challenges in Dog Training and Solutions
- Q&A
- To Conclude
Understanding the Science Behind Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement is a powerful technique rooted in behavioral psychology that encourages desirable behaviors through rewards. This approach hinges on the premise that behaviors followed by rewarding stimuli are more likely to be repeated. When training dogs, positive reinforcement leverages their natural instincts and preferences, creating a more engaging and enjoyable learning experience. By associating good behavior with treats, praise, or playtime, dog owners can effectively shape their pets’ actions in a way that fosters trust and cooperation.
The science behind this method involves operant conditioning, a concept popularized by psychologist B.F. Skinner. Through systematic reinforcement, dogs learn to associate specific actions with positive outcomes. Key elements of successful training sessions include consistency, timing, and specificity. Here are some essential practices to consider:
- Immediate Rewards: Provide reinforcement promptly to create a clear connection between the behavior and the reward.
- Variety of Rewards: Use treats, toys, or attention to keep the dog motivated and engaged.
- Gradual Steps: Start with simple commands and increase difficulty as the dog becomes more proficient.
Exploring the Role of Consistency in Effective Dog Training
When it comes to training dogs, consistency is the cornerstone of effective communication and behavior modification. Dogs thrive on routine and repetition, which helps them grasp expectations and respond appropriately. By establishing clear commands and sticking to them, trainers can create a reliable framework within which dogs learn. This means using the same verbal commands and hand signals every time, ensuring that any desired behavior is consistently rewarded and undesired behaviors are consistently redirected.
- Routine Reinforcement: Utilizing training schedules helps dogs understand what is expected of them.
- Clarity in Commands: Use of distinct and unambiguous commands prevents confusion.
- Positive Reinforcement: Rewarding desired behaviors promptly reinforces learning.
Additionally, consistent training goes beyond the commands themselves; it involves ensuring that all family members and caregivers participate in the same training methods. Mixed signals can easily confuse a dog, leading to frustration for both the pet and the owner. Establishing consistent rules within the household is essential for cohesive training efforts. To illustrate this, consider the following simple guidelines:
| Behavior | Consistent Approach |
|---|---|
| Sit on Command | All family members use “Sit” with the same tone and gesture. |
| No Barking | Everyone responds to barking with the same quiet signal. |
| Potty Training | Frequent outdoor trips at the same times each day. |
Tailoring Training Techniques for Different Breeds and Temperaments
Understanding the unique traits and temperament of different dog breeds is essential when implementing effective training techniques. For example, breeds known for their intelligence, such as Border Collies and Poodles, thrive on complex tasks that challenge their minds. Incorporating interactive toys and obedience games can keep them mentally stimulated. Conversely, more stubborn breeds like Bulldogs may respond better to a straightforward approach that emphasizes consistency and positive reinforcement. Employing methods such as clicker training with frequent rewards can make the learning experience enjoyable and productive for them. Tailoring training styles to suit these diverse needs fosters a more effective learning environment.
Additionally, awareness of a dog’s temperament can significantly enhance training outcomes. Dogs with high energy levels, like Retrievers, benefit from exercise-oriented training sessions that incorporate plenty of movement and play. In contrast, calmer breeds, such as Basset Hounds, may require a gentler approach, utilizing soft-spoken commands and a slower pace. Utilizing a variety of teaching aids and techniques is beneficial, and the following table summarizes some effective strategies for different temperaments:
| Breed Type | Preferred Training Technique | Training Aids |
|---|---|---|
| High-energy | Exercise-oriented sessions | Interactive toys, agility equipment |
| Stubborn | Positive reinforcement | Clickers, treats |
| Calm | Gentle approach | Soft-spoken commands, long lead |
| Intelligent | Complex tasks | Puzzle toys, training games |
Navigating Common Challenges in Dog Training and Solutions
Dog training can be a rewarding yet challenging endeavor. Many owners encounter issues such as lack of focus, stubbornness, or fear that can hinder the training process. To effectively address these hurdles, it is essential to incorporate a combination of positive reinforcement techniques, consistent commands, and patience. When a dog seems unfocused, try engaging them with their favorite toy or treat to refocus their attention. Additionally, establishing a routine with set training times can help create an environment where the dog learns to expect training sessions, making them more receptive to learning.
Another common obstacle in dog training is behavioral issues, such as excessive barking or jumping on people. These behaviors can often stem from boredom or excess energy. Solutions such as structured playtime, socialization, and mental stimulation are key. Implementing activities like puzzle toys or obedience games can keep your dog’s mind active, while regular walks and playdates provide physical exercise and social interaction. Below is a simple table illustrating effective strategies to counter specific behavioral challenges:
| Behavior Issue | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|
| Excessive Barking | Introduce quiet commands and rewards for calm behavior. |
| Jumping on People | Teach “sit” to greet guests politely and rewards for calmness. |
| Chewing Furniture | Provide chew toys and redirect when caught in the act. |
Q&A
Q&A: Understanding Dog Training Methods
Q1: What are the most common dog training methods?
A1: The most common dog training methods include positive reinforcement, clicker training, dominance-based training, and relationship-based training. Each method has its own philosophy: positive reinforcement encourages good behavior through rewards, while dominance-based training often relies on a more authoritative approach. Clicker training uses a sound to mark desired behavior, and relationship-based training focuses on building a bond between dog and owner as the foundation for training.
Q2: How does positive reinforcement work in dog training?
A2: Positive reinforcement works by providing a reward—such as treats, praise, or playtime—immediately after a desired behavior is displayed. This approach helps dogs associate good behavior with positive outcomes, increasing the likelihood that they will repeat that behavior in the future. It’s about creating a positive learning environment where the dog feels motivated to obey.
Q3: What is clicker training, and how is it different from other methods?
A3: Clicker training is a form of positive reinforcement that employs a clicker—a small handheld device that makes a distinct sound— to mark a specific behavior when it occurs. The sound of the click acts as an immediate event marker that tells the dog they’ve done something right, which is then followed up with a reward. This contrast with other methods lies in the precision of timing; the clicker allows for immediate feedback, essential for effective learning.
Q4: Are there any risks associated with dominance-based training?
A4: Yes, dominance-based training can come with risks. This method often involves asserting control over the dog to establish the owner’s position as ‘top dog,’ which can unintentionally lead to fear, anxiety, or aggression in some dogs. Critics argue that this approach may damage the trust between owner and pet, making training less effective in the long run.
Q5: Which training method is best for my dog?
A5: The best training method depends on your dog’s temperament, your goals, and the training environment. Generally, positive reinforcement is widely recommended due to its effectiveness and the loving bond it fosters. However, different dogs respond to different techniques, so it may be beneficial to combine aspects of various methods or consult a professional trainer who can tailor a program suited to your pup’s needs.
Q6: How long does it typically take to train a dog using these methods?
A6: The timeline for training a dog varies widely based on factors like the dog’s age, breed, prior experiences, and the complexity of the desired behavior. Basic commands like “sit” or “stay” may take a few sessions to establish, while more complex behaviors or resolving behavioral issues could require weeks or even months of consistent training. Patience and consistency are key across all methods.
Q7: Can I train my dog on my own, or should I seek professional help?
A7: You can certainly train your dog on your own, especially with the numerous resources available today—books, videos, and online courses. However, if you’re facing specific challenges or if your dog exhibits behavioral issues, seeking professional help may provide invaluable guidance. Trainers can offer personalized strategies, troubleshoot problems, and ensure that both you and your dog enjoy the training process.
Q8: What role does socialization play in dog training?
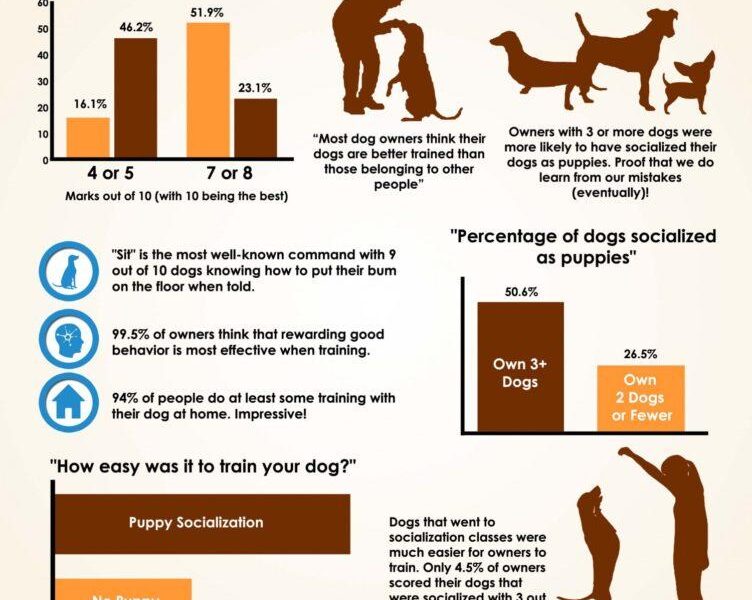
A8: Socialization is a crucial part of dog training as it helps dogs learn how to interact with other animals and people. Early and ongoing socialization can prevent fear-based behaviors and help your dog become a well-adjusted companion. It reinforces commands learned in training, as socialized dogs are often more confident and responsive in various environments.
By understanding these fundamental elements of dog training, you can enhance your relationship with your furry friend while fostering the skills necessary for a well-behaved companion. Each method has its unique attributes, and the key is to find the best fit for you and your dog. Happy training!
To Conclude
navigating the world of dog training methods can feel like a daunting task, but it ultimately boils down to understanding the unique needs of your canine companion. Whether you opt for positive reinforcement, clicker training, or a balanced approach, the key is consistency, patience, and a willingness to adapt. Remember, every dog is an individual, and there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. By fostering a strong bond built on trust and communication, you not only teach your dog valuable skills but also enrich your relationship. As you embark on this rewarding journey, embrace the learning process—for both you and your furry friend—and celebrate each small victory along the way. Happy training!